The key to managing semaglutide side effects lies in proactive dietary adjustments and metabolic pacing. Most common gastrointestinal issues are self-limiting, subsiding as your system acclimates to the medication’s effect on gastric motility.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Semaglutide, the active ingredient in medications like Ozempic, Wegovy, and Rybelsus, commonly causes gastrointestinal issues.
The arrival of GLP-1 medications has transformed the treatment of obesity and metabolic dysfunction. However, as with any systemic medical intervention, the journey is rarely without its hurdles.
Side effects of Semaglutide generally range from mild to moderate, but sometimes when left untreated serious complications can occur.
Understanding Semaglutide side effects is the difference between a patient who quits in week three and one who achieves a life-changing transformation.
In 2026, we no longer view side effects as “necessary evils.” Instead, we view them as biological feedback. GLP-1 Medication and GI Side Effects: Nausea, Constipation, and Bloating
This guide will walk you through the most common challenges—from the “Ozempic burp” to the dreaded “metabolic shed”—and provide clinical protocols to master your internal chemistry.

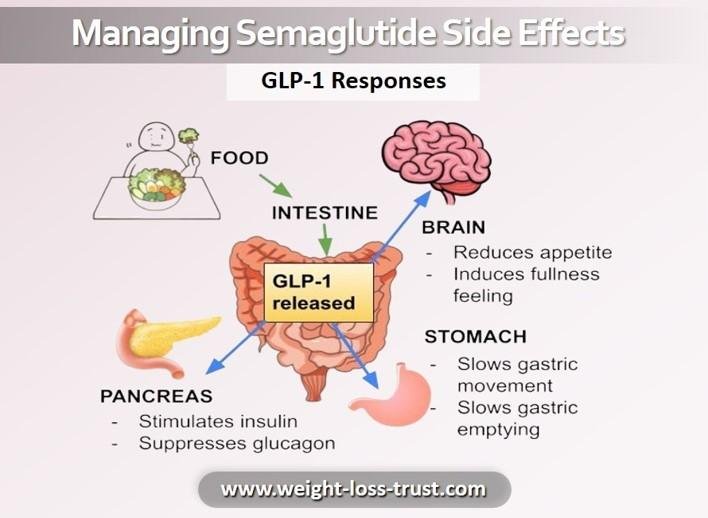
The Spectrum of GLP-1 Responses
While the physiological shift can feel daunting, it is not a reason for cessation, but a call for clinical strategy.
To bridge the gap between initial discomfort and metabolic steady-state, we must look beyond the prescription.
Managing semaglutide side effects effectively requires mastering three core pillars:
- Gastric motility support,
- Hydration electrolyte balance, and
- Metabolic pacing.
Semaglutide, the active pharmaceutical ingredient in GLP-1 medications including Ozempic, Wegovy, and Rybelsus, is clinically associated with a range of gastrointestinal side effects.
When you introduce a GLP-1 receptor agonist into your system, you are essentially mimicking a hormone your body produces naturally after a meal. Because these receptors are located throughout the digestive tract and the brain, side effects of Semaglutide can manifest in various systems.
Most symptoms are “titration-dependent,” meaning they occur most frequently when you increase your dosage.
By following a “Low and Slow” protocol, many of the most uncomfortable Semaglutide side effects can be mitigated or avoided entirely.
Further Reading: Don’t let digestive discomfort stall your progress. Master your gut health with our deep dive into GLP-1 Medication and GI Side Effects: Nausea, Constipation, and Bloating.
Clinical Safety
The Expert Proof: While these management strategies are highly effective, they will not work if the user is in a caloric deficit below 1,000 calories. At that level of deprivation, the body enters a starvation response that no amount of lifestyle adjustment can override.
Common Semaglutide Side Effects
The clinical incidence of gastrointestinal distress is most prevalent during the initial titration phase of Semaglutide therapy; however, these symptoms typically resolve as the body achieves metabolic steady-state and physiological adaptation occurs.
- Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
- Abdominal pain or cramping
- Constipation
- Heartburn, burping, gas, or bloating
- Loss of appetite
- Headache
- Fatigue or dizziness
- Runny nose or sore throat (less common)
Rare but Serious Semaglutide Side Effects and Warnings
Clinical vigilance is required for the subset of serious adverse events that, while statistically rare, demand immediate medical triage and diagnostic assessment.
- Thyroid tumors/cancer: Semaglutide has a boxed warning for the potential risk of thyroid C-cell tumors, including medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC), observed in rodent studies. It is unknown if this occurs in humans. Symptoms include a lump in the neck, trouble swallowing, hoarse voice, or shortness of breath.
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas. Symptoms include severe pain in the upper stomach radiating to the back, nausea, and vomiting.
- Gallbladder problems: May cause gallstones or inflammation of the gallbladder, with symptoms like upper stomach pain, fever, jaundice (yellow skin/eyes), or clay-colored stools.
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar): This risk is higher if semaglutide is used with other diabetes medications like insulin or sulfonylureas. Symptoms include sweating, shakiness, confusion, irritability, headache, and a fast heartbeat.
- Kidney injury: Dehydration from severe vomiting or diarrhea can lead to kidney problems.
- Severe allergic reactions: Symptoms include hives, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, and difficulty breathing.
- Vision changes: Worsening of diabetic retinopathy has been reported.
1. Gastrointestinal Mastery: Nausea and Reflux
The most frequently reported Semaglutide side effects are nausea and acid reflux. Because the medication slows gastric emptying (the speed at which food leaves your stomach), eating a large or high-fat meal can lead to significant discomfort.
- The 2026 Protocol: Shift to “Mechanical Eating.” Eat small, dense meals every 3–4 hours rather than three large ones.
- The Ginger/Artichoke Shield: Prokinetic supplements like ginger and artichoke extract can help move food through the stomach more efficiently, reducing the “heavy” feeling often associated with Semaglutide side effects.
2. The “Ozempic Burp” and Bloating
Slower digestion means food sits in the stomach longer, where it can begin to ferment. This leads to the infamous “sulfur burps.”
- The Fix: Eliminate carbonated beverages and cruciferous vegetables (like raw broccoli) during the first 48 hours after your injection. This simple shift can reduce the gas-related Semaglutide side effects significantly.
3. Metabolic Fatigue and Energy Dips
Many users report feeling “wiped out” during the first few months. This isn’t usually the drug itself, but rather a “fueling gap.”
When your appetite vanishes, you may inadvertently drop below 1,000 calories a day, leading to hypoglycemia or general lethargy.
- The Fix: Prioritize electrolyte-rich hydration. GLP-1s can increase the excretion of sodium, so adding a high-quality electrolyte powder to your water can resolve the “brain fog” often labeled as one of the common Semaglutide side effects.
4. The Aesthetic Challenge: GLP-1 Hair Loss
One of the most distressing Semaglutide side effects is the temporary thinning of hair, known as Telogen Effluvium. This happens when the body prioritizes vital organs over “luxury” tissues during rapid weight loss.
- To learn how to stop this specific issue, read our comprehensive guide on GLP-1 hair loss and the Micronutrient Shield protocol.
Effects of Weight Loss (“Ozempic Face/Feet”)

Rapid weight loss can lead to cosmetic changes such as sagging skin or loss of facial volume, often referred to as “Ozempic face”.
Similarly, “Ozempic feet” can involve a loss of fat padding on the soles, causing discomfort when walking.
Evidence suggests these clinical observations are symptomatic of systemic metabolic adaptation to caloric restriction, rather than a direct toxicological consequence of the drug’s chemical constituents.
In other words, “Ozempic face” and Ozempic feet” are results of weight loss itself rather than the chemical properties of the drug.
Further Reading: Don’t let rapid fat loss compromise your skin. Combat Ozempic face by prioritizing dermal density. Clinical collagen supplementation is the smartest way to support skin elasticity and facial volume, preventing rapid weight loss from sabotaging your aesthetic results.
Goodbye ‘Ozempic Face’: The Best Collagen for Ozempic Face 2025
General Management Strategies
- Gradual Dose Increase: The best strategy for minimizing side effects is to start with a low dose and increase it gradually over time, as directed by a healthcare provider.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water and clear fluids throughout the day. Dehydration can worsen several side effects, including nausea, headaches, and constipation.
- Eat Small, Frequent Meals: Opt for smaller portions and more frequent meals throughout the day instead of three large ones. This can help manage nausea and fullness.
- Modify Diet: Avoid high-fat, fried, greasy, or very sugary foods, as these can exacerbate gastrointestinal issues. Focus on bland, nutrient-dense foods, lean proteins, and complex carbohydrates.
- Prioritize Activity and Sleep: Gentle physical activity, like walking after meals, can aid digestion and boost energy. Ensure adequate sleep to help your body adjust.
- Consult Your Healthcare Provider: If side effects are severe, persistent, or interfering with daily life, contact your healthcare team. They can adjust your dose, suggest prescription remedies, or consider switching medications.
While many patients adapt quickly, others require a more granular approach to digestive health. For a detailed breakdown of clinical protocols, explore our specialized guide on GLP-1 Medication and GI Side Effects: Nausea, Constipation, and Bloating to master your daily comfort.
Specific Side Effect Management
| Side Effect | Management Strategies |
|---|---|
| Nausea | * Eat bland, low-fat foods (crackers, rice, toast). * Try natural remedies like ginger tea or supplements. * Avoid lying down immediately after eating. * Your doctor may prescribe anti-nausea medication like ondansetron (Zofran). |
| Constipation | * Increase water and fiber intake gradually through diet (fruits, vegetables, whole grains) or supplements. * Stay physically active. * OTC medications like polyethylene glycol (MiraLAX) or stool softeners may be recommended by your provider. |
| Diarrhea | * Drink plenty of water and low-sugar electrolyte drinks to replace lost fluids. * Follow the BRAT diet (bananas, rice, applesauce, toast) temporarily. * Avoid high-fat foods, dairy, caffeine, and alcohol. * OTC anti-diarrheal medication like loperamide (Imodium) can be used after consulting your provider. |
| Headache/Dizziness | * Ensure adequate hydration, as these can be signs of dehydration. * Check blood sugar levels if you have diabetes and eat a snack if low. * OTC pain relievers (acetaminophen or ibuprofen) can provide relief. |
| Fatigue | * Eat nutrient-dense foods in smaller, more frequent meals to maintain steady energy levels. * Prioritize quality sleep and gentle exercise. * Ensure you are adequately hydrated. |
| Gas/Bloating | * Chew food thoroughly and eat slowly. * Avoid carbonated beverages and gas-producing foods like beans, lentils, and cabbage. * OTC products like simethicone (Gas-X) can help. |
FAQ – (Frequently Asked Questions) Semaglutide Side Effects
The “Titration Hygiene” Checklist
To minimize Semaglutide side effects, follow this 2026 checklist before every injection:
- Hydrate+: Drink 16oz of water with electrolytes 2 hours before your shot.
- Protein First: Ensure your last meal before the injection is lean protein (chicken, white fish, or tofu).
- The Sleep Window: Many users find that taking their injection before bed allows them to “sleep through” the initial peak of nausea.
- Avoid “The Big Three”: No fried foods, no high-sugar treats, and no alcohol for 24 hours post-injection.
Final Verdict
In conclusion, effective management of semaglutide’s predominantly mild-to-moderate gastrointestinal side effects relies on a proactive, multidisciplinary approach.
Key strategies integrate gradual dose escalation, targeted dietary and lifestyle changes, and close communication with a healthcare provider to ensure adherence and optimize therapeutic outcomes.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical care if you experience severe symptoms such as signs of an allergic reaction (swelling, trouble breathing), severe abdominal pain that doesn’t go away or radiates to your back, continuous vomiting, or symptoms of severe low blood sugar (confusion, slurred speech, cold sweats).
Additional Reading:
- The Clinical Guide to Best Digestive Enzymes for Ozempic (2025)
- Banish Ozempic Fatigue: The 5 Best Electrolytes to Reclaim Your Life
- 1st Phorm vs. Vital Proteins vs. Vida Glow: The Best Collagen for Ozempic Face Comparison (2025)
- Unlock: Why Muscle Preservation on Ozempic is the Real Secret to Staying Lean 2025
- Best GLP-1 Meal Delivery Services: High Protein Plans for Ozempic & Wegovy Success